Whether you’ve previously been pregnant or this is your first time, you’re probably going to great lengths to ensure pregnancy health. But are you taking care of your emotional and mental health? The physical well-being of the fetus is closely tied to your pregnancy health. But now, a recent study has linked maternal mental health to the child’s language acquisition. Researchers have found that depression during pregnancy can negatively impact a baby’s early language development.
Speech Delays in Children: Could it Be Neurofibromatosis?
Speech DisordersIf you’ve spent any amount of time researching disorders and speech delays in children, you probably already know how easy it is to acquire a slight case of hypochondria. And if you’re a parent, you may know just how easy it is to become a hypochondriac by proxy. You want the best for your child, so you do some in-depth investigating on WebMD or the Mayo Clinic’s website into every sniffle and sneeze. But sometimes a seemingly innocuous issue like a communication problem really can be a sign of a more serious medical condition. Speech delays in children should be evaluated by a licensed speech-language pathologist (SLP). If your child has speech and language problems, and also has other symptoms like multiple birthmarks and skeletal abnormalities, he may also need to be evaluated for neurofibromatosis.
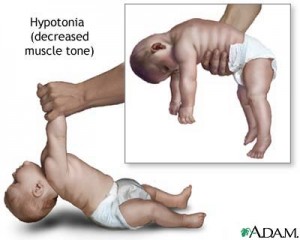
Coping with Hypotonia
Language DevelopmentWhat Is It?
Hypotonia is a condition in which the patient has poor or decreased muscle tone. This is not the same as muscle weakness; however, patients with hypotonia often do have weaker muscles. With hypotonia, the brain fails to transmit the proper electrical signals to the muscles that tell them to contract. Hypotonia may be present in varying degrees of severity. It can be caused by a wide range of diseases and conditions, including muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, trauma, and genetic disorders.